Key Points:
COVID
- In today’s Recommendation for Industry, we discuss the alternating status of monkeypox and Covid. Read more below.
- FDA authorizes updated COVID boosters from Moderna and Pfizer. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that it has authorized for emergency use bivalent booster shots that target the Omicron BA.4/BA.5 subvariants. The FDA specifically approved Moderna’s bivalent vaccine for individuals 18 and older and Pfizer/ BioNTech vaccine for people ages 12 and older. Doses should be ready to be delivered sometime in September. The FDA based its authorization on clinical data from trials for a bivalent booster targeting the BA.1 Omicron subvariant, as well as preclinical data on the BA.4/BA.5 version and earlier data from primary vaccination and booster trials. The World Health Organization has said that cases and deaths declined last week. With cases declining, BA.5’s prevalence is still rising and currently makes up 78.2% of cases.
- SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in kids after COVID may peak at 1 to 3 months. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics released data showing that children 0 to 16 years old had SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody levels that peaked at 84% 1 to 3 months after they tested positive for COVID. In addition, those antibody levels remained high for more than a year after. The antibodies were found to be at 70% at 9 to 13 months.
- Chengdu locks down 21.2 million people as Chinese cities battle Covid-19. One of China’s biggest cities, Chengdu has announced its lockdown for 21.2 residents as it has launched a four-day citywide COVID-19 testing as outbreaks are occurring throughout their economically important urban centers. This comes from a report of 157 domestically transmitted infections on Wednesday. Residents are allowed to send on person from their household a day to shop for necessary items. Non-essential employees in Chengdu were asked to work from home and residents were urged not to leave the city unless needed. Residents who must leave their residential compounds for hospital visits or other special needs must obtain approval from neighborhood staffers.
Monkeypox
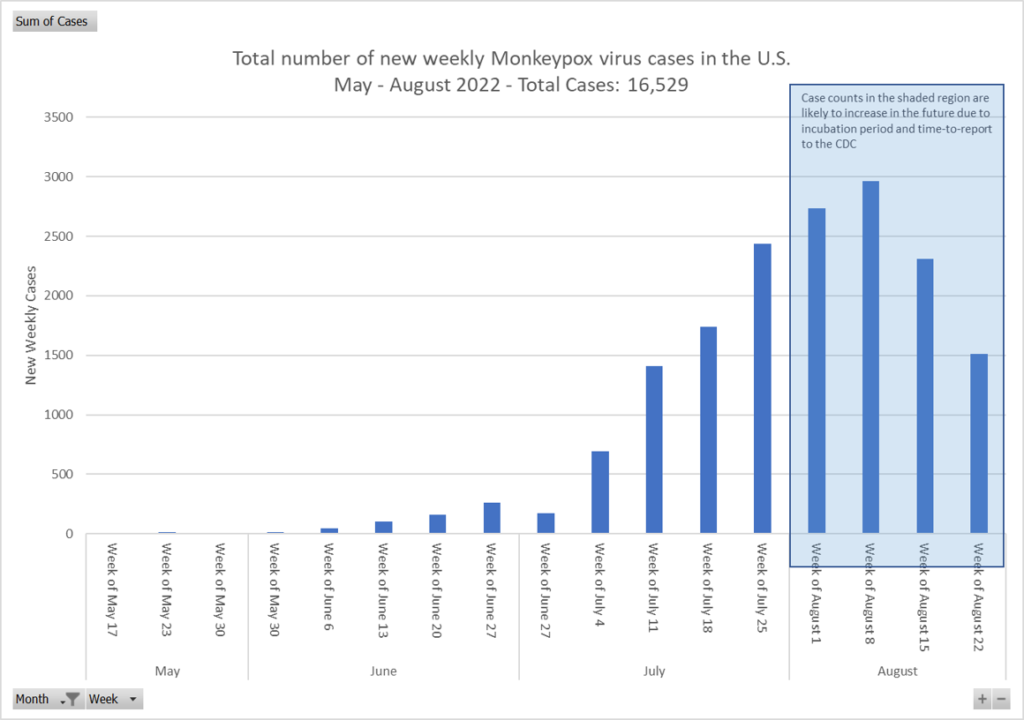
- Texas reports first presumed US monkeypox death. The individual who is reported as the first US fatality was from Harris County, Texas, and was severely immunocompromised. Health officials, despite the recent fatality, continue to state that death caused by monkeypox is rare. In global news, Brazil has reported its second monkeypox death, involving a 33-year-old man who had underlying health conditions. The US total currently reported by the CDC is at 18,989 cases.
Food Safety & Public Health
- September 2022 is the 24th National Food Safety Education Month. This month takes a role in preventing foodborne illness. Every year there are approximately 48 million cases of foodborne illness- 1 in 6 Americans each year. Here are some resources for simple food safety tips that can help lower your chance of getting sick:
- Food Safety Month begins with risk-reducing home handling tips for poultry– Don’t Wash Your Chicken is a collaboration launched by Drexel University and New Mexico State University to educate people on preparing chicken at home. Recent research found that home cooks continue to wash raw poultry because they desire to control the process of preparing food, lack of trust in chicken processing, and the habitual nature of the behavior. Research also revealed that home cooks are willing to change their behavior if they understand the “why” behind the guidance. This program aims to help people understand how chicken is processed before they get it, learn the risks of washing raw poultry, as well how to safely handle and cook poultry at home. The three main takeaways from this program are that washing and rinsing chicken increases the risk of spreading bacteria, chicken has already been washed, and there’s a better and safer way to cook chicken.
- FDA looking into new outbreak, along with 10 other ongoing investigations. A new outbreak reported on August 31st, but not yet posted by the CDC is around Salmonella findings in Mississippi. This outbreak accounts for 99 of 1,350 currently sickened people due to outbreaks in the US. There is no further information on this outbreak currently. The FDA has initiated sample and collection analysis in response to the E. coli 0157 outbreak related to the lettuce of Wendy’s sandwiches. The CDC has reported 84 individuals that have become ill related outbreak.
Recommendations for Industry
The Ups and Downs of Today’s Communicable Diseases
Communicable diseases continue to be at the top of the news – and the top of TAG’s business recommendations. With TAG’s weekly matrix continuing to show Covid having a gradual, but steady decline across much of the U.S., the counter to that are the indications of a gradual, but steady incline of the monkeypox statistics in the U.S.
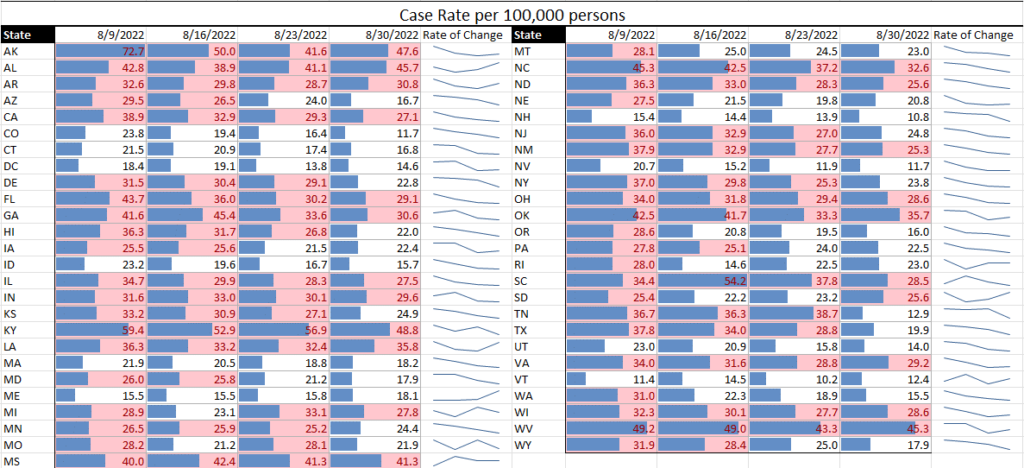
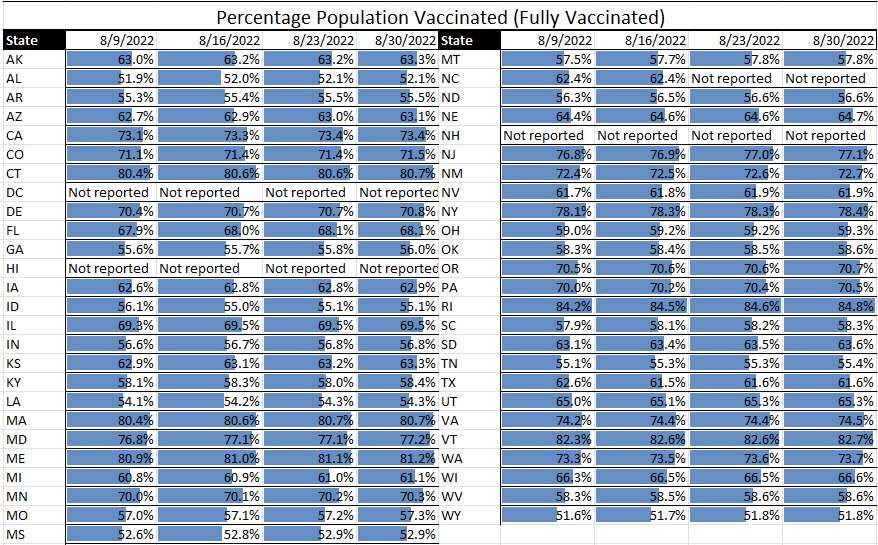
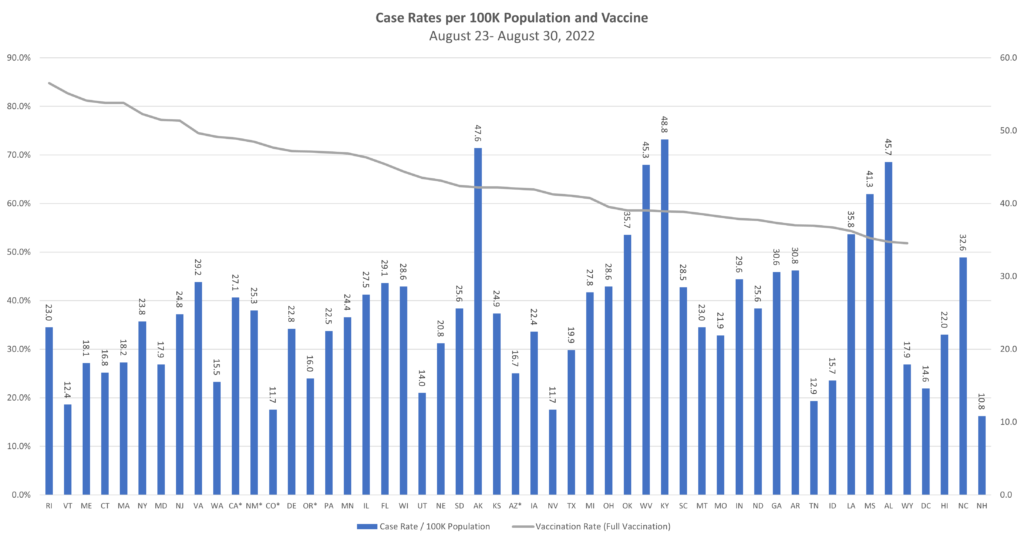
Covid. Although a few specific states continue to see high or even somewhat increased rates of Covid transmission (e.g., Rhode Island), the overall trend is that of decreasing transmission and case rates. Regarding hospitalization rates, there are some states still in the red, but we’ve seen some states move from yellow to green, and none move from green to yellow or yellow to red – a very good sign.
Monkeypox. Although there is not much change from last week, we are seeing a slightly upward trend, and expecting that the delayed reporting of the last two will show a similar trajectory once reported. There are currently 18, 989 cases in the U.S. according to the CDC with Texas reporting of the first fatality, though the person had significant underlying conditions.
Communicable diseases have always been a part of our lives and will continue to be. But having lived and learned through the pandemic, we now have more applied knowledge of prevention and control that can assist us in all such diseases … including the flu, which we will once again be reporting on and making recommendations for, beginning next week. Keep an eye on this space and give TAG a call for any assistance you may need.
Risk Matrix
COVID
Monkeypox
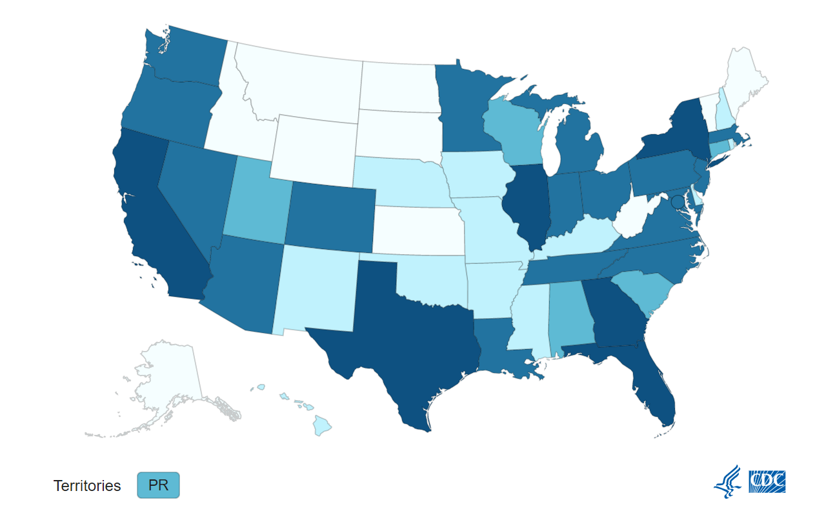

In case you missed it:
COVID
- In Tuesday’s Recommendation for Industry, we discussed 2022-23 U.S. Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Overview. Read more here.
- Paxlovid, molnupiravir benefit older COVID-19 patients, 2 studies show. One from Israel suggesting that nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) reduced rates of hospitalization and death in people 65 years or older, and research from Hong Kong demonstrating that Paxlovid and molnupiravir lowered rates of death, disease progression, and the need for supplemental oxygen in older hospitalized patients. Within the US, the FDA has granted emergency use of oral Paxlovid and molnupiravir for treatment of patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 at high risk for severe illness within 5 days of symptom onset.
- mRNA COVID vaccines protect against severe Omicron for at least half a year. Researchers at the National Centre for Infectious Diseases in Singapore studied the effectiveness against infection and severe illness of two or more doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna mRNA COVID-19 vaccines or the inactivated Sinovac, CoronaVac, or Sinopharm Chinese COVID-19 vaccines in 2,441,581 residents aged 30 years or older from Dec 27, 2021, to Mar 10, 2022. Among the 2,441,581 participants, 319,943 (13.1%) tested positive for COVID-19, and 1,513 (0.4%) were severe infections. Estimated vaccine effectiveness (VE) of an mRNA booster against Omicron infection was 31.7% to 41.3% after 15 to 60 days and waned rapidly over time. Estimated mRNA booster VE against severe COVID-19 was 87.4% and didn’t wane for up to 6 months. The estimated VE of three doses of inactivated vaccine against severe illness was 69.6%.
Monkeypox
- Monkeypox epicenter moves from Europe to Americas. Monkeypox transmission has dropped in Europe, was the initial epicenter of the current outbreak, but now cases are rising in the Americas, making the region the hot spot. As of Aug 22, 41,664 laboratory-confirmed cases of monkeypox and 12 deaths have been reported to the WHO from 96 countries and territories. The average age of monkeypox case-patients is 36, and 98.2% of cases worldwide are in men. Among all cases with sexual identity information provided, 95.8% identify as men who have sex with men (MSM). Sexual transmission was noted among 82.1% of cases, with 60.6% of case-patients likely exposed in a party setting with sexual contacts. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) yesterday reported 694 new US case, raising the national total to 18,101. Four pediatric cases were reported in the country last week, including a child from California and 3 from Georgia. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this week warned that fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) donors should be screened for monkeypox, as rectal swabs show the presence of the virus.
- CDC survey shows changing sexual behaviors in light of monkeypox. Half of US men who have sex with men (MSM) are changing their sexual behaviors because of the monkeypox outbreak, according to a new survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and published today in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). From Aug 5 to Aug 15, 824 men MSM completed an online survey on sexual behavior, and 48% reported reducing their number of sex partners, 50% reported reducing one-time sexual encounters, and 50% reported reducing sex with partners met on dating apps or at sex venues since learning about the monkeypox outbreak. Of the survey participants 1 in 5 said they had received at least one dose of the Jynneos monkeypox vaccine. Vaccine uptake was highest among Hispanic or Latino men (27.1%), and lowest among Black men (11.5%).
- HHS announces $11 million to speed up monkeypox vaccine production. The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced that it will provide about $11 million to support the first US-based fill-and-finish effort of Bavarian Nordic’s monkeypox vaccine. The support will allow production to begin later this year, months ahead of the 9-month timeline typical for starting up fill-and-finish operations. In July, HHS placed orders for 5 million vials of Jynneos from its earlier bulk vaccine order stored in Denmark. And as part of the contract, Bavarian Nordic agreed to a technology transfer that would allow a US-based contract manufacturer to fill and finish 2.5 million Jynneos vials.
Food Safety & Public Health
- Patient count in outbreak linked to Daily Harvest frozen food continues to climb. The number of people with “adverse reactions” to frozen crumbles from Daily Harvest has tripled since the FDA first reported illnesses related to the product in late June. As of Aug. 25, the Food and Drug Administration had received 369 reports of illnesses from consumers. The outbreak is linked to Daily Harvest brand frozen French lentil and Leek crumbles.
- FAO guidance supports the move to digital food control. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) issued guidance on how to design and implement a food control electronic notification system, taking into account a country’s needs and resources. It covers the system’s legal basis, structure, and operational points, as well as the infrastructure and human resource requirements. E-notification systems facilitate the distribution of information on border rejections and product withdrawals helping authorities, companies, and consumers to take action. However, they require a reliable internet connection, which is not available in every country.
- Amaranth Grain recalled in 17 states because of Salmonella contamination. Bob’s Red Mill Natural Foods Inc., of Milwaukie, OR, is recalling Bob’s Red Mill brand Organic Amaranth Grain Gluten Free because of potential Salmonella contamination. The product was distributed in California, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, North Carolina, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Nevada, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Texas and Washington, as well as internationally in the Philippines. To find the specific product recalled click here.
- Hepatitis A cases in Hungary prompt berry mix recall. A berry mix has been recalled across Europe after a number of people were sickened in Hungary by Hepatitis A. Ten to 15 people in Hungary were hospitalized after eating at a restaurant and subsequent testing by a Hungarian laboratory found Hepatitis A in a 2.5-kilogram bag of the berry mix. Ardo’s Fruitberry mix is produced and packed by a subcontractor of the group in Poland. Countries listed in a Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) notification as being sent affected product include Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Ireland, Netherlands, Romania, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom.






